# list with odd and even numbers
lisst = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 31, 17, 70]
# using list-comprehension to select only odd numbers
double_odd = [2*i for i in lisst if i%2==1]
double_odd[2, 6, 10, 62, 34]Ismail TG
October 26, 2022
Q1:
How is a grayscale image represented on a computer? How about a color image? ___ * Grayscale image is way of turning an array/tensor to grayscale value on each pixel of that image, the values went from 0 to 256, the darker the pixel the closer to 256.
Q2:
How are the files and folders in the MNIST_SAMPLE dataset structured? Why?
___
* MNIST_SAMPLE contains two folders Train and Valid.
* This method of structuring dataset help the community to compare the results between models by setting the same framework.
Q3:
Explain how the “pixel similarity” approach to classifying digits works.
___
* First we turn images in tensor, then we stack them together. * we take the mean value of each pixel for all images, this will give us an image that each pixel of it represent the mean of all datset. * Then we classify images by comparing the mean absolute error between that image and the ideal3/ideal7 and see which return low distance.
Q4:
What is a list comprehension? Create one now that selects odd numbers from a list and doubles them.
___
# list with odd and even numbers
lisst = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 31, 17, 70]
# using list-comprehension to select only odd numbers
double_odd = [2*i for i in lisst if i%2==1]
double_odd[2, 6, 10, 62, 34]Q5:
What is a “rank-3 tensor”?
___ * It’s a tensor with 3 dimensions, each can be represented as an array (array of array of array), it’s basically a cube.
Q6:
What is the difference between tensor rank and shape? How do you get the rank from the shape?
____
* Rank represent the dimesion of the tensorm while shape tells how many elemen there’s in each dimension.
Q7:
What are RMSE and L1 norm?
___
* RMSE also called L2 stands dor Root Mean Square Error, while L1 is Least Absolute Error. * This functions are basically the same, we used them to measure distance.
Q9:
Create a 3x3 tensor or array containing the numbers from 1 to 9. Double it. Select the bottom right 4 numbers.
___
tensor([[1., 2., 3.],
[4., 5., 6.],
[7., 8., 9.]])Q10:
What is broadcasting?
___
* It refers to mathematical operation between different dimensions arrays and tensors.
Q11:
Are metrics generally calculated using the training set, or the validation set? Why?
_____ * Metrics are calculated on validation set, so we have good measure of the model performance.
Q12&13:
What is SGD?
Why does SGD use mini-batches?
____ * SGD or Stochastic Gradient Descent is an optimization function that help us to update weights and minimize the loss. * SGD updates gradients after each mini batch, otherwise it will take a lot of time if we decide to update the gradients after going through all the dataset, or the model won’t learn much if we decide to updates the gradients after each data point.
Q14:
What are the seven steps in SGD for machine learning?
___
* Initialize the parameters * Calculate the predictions * Calculate the loss * Calculate the gradients * Step the weights * Redo the whole process from step 2 * Stop
Q15:
How do we initialize the weights in a model?
___
* Usually we initialize weights by picking random values
Q16:
What is “loss”?
___
* The loss is function that uses the model in order to optimizes it’s predictions
Q17:
What’s the gradients?
___
* The gradients are values that dictate how much should we change the weights in order to minimize the loss
Q18:
Why can’t we always use a high learning rate?
___
* Picking a large learning rate will get the loss worse.
Q19:
Do you need to know how to calculate gradients yourself? ___
* It’s important to understand the math behind each concept in Deep Learning, but we don’t need to do everything by ourself, we could use frameworks like pytorch and fastai.
Q20:
Why can’t we use accuracy as a loss function?
___
* Loss function changes as the weights changes, but the accuracy only changes when the predictions change.
Q21:
Draw the sigmoid function. What is special about its shape?
___
* Sigmoid takes an input and return a number always between 0 and 1.
Q22:
What is the difference between a loss function and a metric?
___
* Loss is what model uses to optimize the predidictions, while metrics is what we (the ML practitioner) use to understand the performance of the model.
Q23:
What is the function to calculate new weights using a learning rate?
___
* The optimizer function
Q24:
What does the DataLoader class do?
___ * Can be used to iterate through data, create batches, transform data..
Q25:
Write pseudocode showing the basic steps taken in each epoch for SGD.
____
predictions = linear_model(x)
loss = mnist_loss(predictions, y)
loss.backward()
for parameter in parameters:
parameter.data -= parameter.grad.data * learning_rate
parameter.grad = NoneQ26:
Create a function which, if passed two arguments [1,2,3,4] and ‘abcd’ , returns [(1, ‘a’), (2, ‘b’), (3, ‘c’), (4, ‘d’)] . What is special about that output data structure?
___
inputs = [1, 2, 3, 4]
labels = ['a', 'b', 'c', 'd']
def data_func(xb, yb):
return list(zip(xb, yb))
data_func(inputs, labels)[(1, 'a'), (2, 'b'), (3, 'c'), (4, 'd')]Q27:
What does view in Pytorch do? ____
* It changes the shape of the tensor without changing it content.
Q28:
What are the “bias” parameters in a neural network? Why do we need them?
___
* Bias allow us to all kind of multiplications without thinking if the inputs are zero in some cases.
Q29:
What does the @ operator do in Python?
___
* In python @ is used to do matrix multiplication.
Q30:
What does the backward method do?
___ * Backward tells pytorch to calculate the change in the gradients at that point
Q31:
Why do we have to zero the gradients?
___ * zero gradients tell pytorch to not track the changes in gradients while we updates the weights.
Q32:
What information do we have to pass to Learner?
___ * things we pass to Learner : - DataLoaders - architecture - loss_func - metrics
Q33:
Show Python or pseudocode for the basic steps of a training loop.
____
def train_epoch(model, lr, params):
for xb,yb in dl:
calc_grad(xb, yb, model)
for p in params:
p.data -= p.grad*lr
p.grad.zero_()
for i in range(5):
train_epoch(model, lr, params)
Q34:
What is “ReLU”? Draw a plot of it for values from -2 to +2.
___ * ReLU stands from Rectified Linear Unit. This non-linear finction return any negative activations into zero. 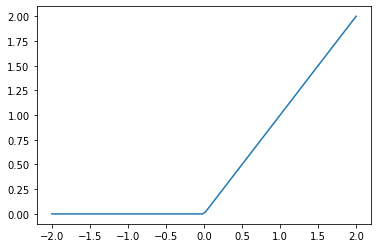
Q35:
What is an “activation function”?
___ * An activation function is a non-linear function that takes the outputs activations fron one layer of the neural network as inputs and output it after some kind of computation to another layer o NN.